The data below indicates AACPS’ progress toward the goals as stated in this Priority area of the Strategic Plan.
To view a scorecard document that shows AACPS’ progress toward all five goals, click here.
Goal A
Increase the percent of students ready to transition to Kindergarten for all student groups as measured by the MSDE Kindergarten Readiness Assessment.

Black/African American | Hispanic | Multiracial | White | Special Education | English Learners | Economically Disadvantaged |
37% | 26% | 48% | 56% | 19% | 10% | 28% |
Note: MSDE did not administer KRA in fall 2024. Groups ≥ 5% of the student population are displayed. Fall 2025 results expected December 2025.
Goal B
Increase the percent of students who access and demonstrate success in Career and Technical Education (CTE), Cultural Arts, Advanced Placement (AP), International Baccalaureate (IB), or Dual Enrollment programs (as defined by MSDE) for all student groups.
Goal C
Increase the percent of students who graduate high school in four years for all student groups.
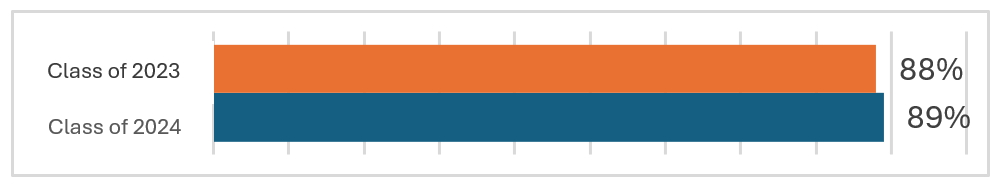
Student | Black/African | Hispanic | Multi-Racial | White | Special Education | English Learners | Economically Disadvantaged |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Class | 84% | 75% | 90% | 93% | 65% | 56% | 83% |
Class | 87% | 78% | 91% | 93% | 72% | 61% | 86% |
Next Update: February 2026
Abbreviations and Notes
ES: Elementary Schools
MS: Middle Schools
HS: High Schools
Economically disadvantaged, rather than FARMs, is reported as in ESSA
Groups > 5% of the student population are displayed.
KRA: Kindergarten Readiness Assessment is an assessment tool used by the Maryland State Department of Education (MSDE) to measure a child's readiness for kindergarten. The KRA is part of the Ready for Kindergarten (R4K) assessment system, which is designed to help identify the supports children need to succeed in school. The KRA assesses a child's skills and abilities in four areas: Social foundations, Language and literacy, Mathematics, and Physical well-being and motor development.
CTE Concentrator: A CTE Concentrator is typically the third course of a CTE completer program. In addition to being enrolled in the concentrator level course, the student must have passed the prior two courses in the aligned program.
CTE Completer: Students who have completed an approved CTE program of study, typically four credits in each CTE program area.
Industry Recognized Certifications are a formal validation of an individual’s skills and/or competencies that align with state or regional in-demand occupations and are recognized by industry and employers. An Industry Recognized Certifications may be a certification, license, or credential obtained through an assessment process, is portable, and may be stackable. The Industry Recognized Certification leads to documented positive employment outcomes, ensures relevance in the labor market, and supports career advancement and economic development for credential holders. The first four industry certifications for any student are considered and aligned with an MSDE-approved CTE program and achieved CTE concentrator level status or higher.
Dual Enrollment is a program offered by a partnership between at least one institution of higher education and at least one local school system through which a secondary school student who has not graduated from high school with a regular high school diploma can enroll in one or more postsecondary courses and earn postsecondary credit that is transferable to the institutions of higher education in the partnership; and applies toward completion of a degree or recognized educational credential as described in the Higher Education Act of 1965 (20 U.S.C. 1001 et seq.).
Dual Enrollment Credit is earning credit (A, B, C, D, or Satisfactory) in at least 1 dual enrollment course.
AP: Advanced Placement courses are courses that meet a prescribed syllabus developed by the College Board. These courses represent college level study and prepare students to take a college level examination in May. Access is taking a course. Success is earning a 3 or higher.
IB DP: International Baccalaureate Diploma Bound courses fall into six subject groups, including studies in language and literature, language acquisition, individuals and societies, sciences, mathematics, and the arts. Most subjects can be taken at either standard level (SL) or higher level (HL), and students must take at least three subjects at HL to earn the diploma. Access is taking a course. Success is earning a 4 or higher.
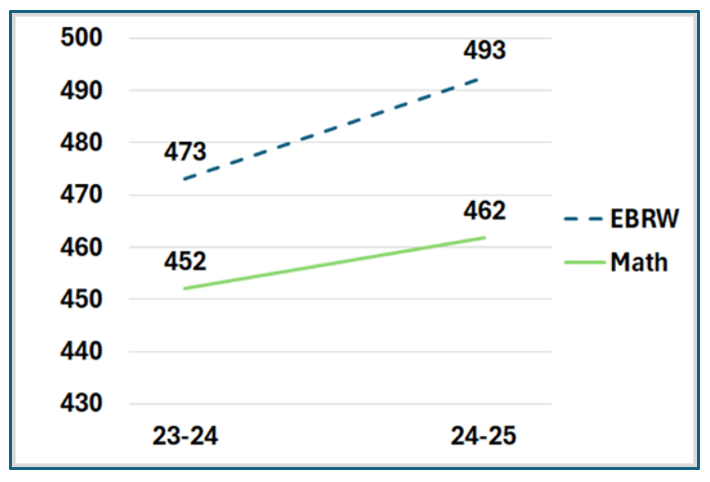
PSAT/NMSQT is a standardized assessment closely connected to the SAT and cosponsored by the College Board and the National Merit Scholarship Corporation. It’s typically given to 11th graders. If a student earns a high score on the PSAT during their junior year, they can qualify to receive a National Merit Scholarship. It tests skills in evidence-based reading/writing (EBRW), and math, ranging from 160-760 for each section. Unlike the SAT, the highest score possible on the PSAT is 1520.
SAT is a standardized college admissions test widely used. It's designed to assess high school students' readiness for college and provide colleges with a common data point to compare applicants. Most students take the SAT during their junior or senior year of high school. Section scores (Math and Evidence-Based Reading/Writing [EBRW]) are reported on a scale of 200 to 800. A total score for the SAT is calculated by adding the two section scores, resulting in total scores that range from 400 to 1600.
Graduation Rate: The 4-year adjusted cohort graduation rate is the percentage of a school's cohort of first-time 9th grade students who graduate within four years, adjusted for students who transfer in and out of the cohort after 9th grade.